Terms and Cuts
Bevel The small gap between floor or wall boards.
Heartwood The dense inner core part of a tree trunk, yielding the hardest timber for lumber and flooring.
Sapwood The soft outer layers of recently formed wood between the heartwood and the bark, that gives the floor or wood its unique character look.
Paneling v Siding Paneling usually refers to wood inside like Wallboarding or bead boards whereas Siding refers to the same for exterior applications.
ECB Edge and Center Bead, a type of pattern with siding.
Patina The unique inherited color of the wood that can be drawn out by finished like Tung Oil.

Live Sawn
Live Sawn lumber is produced by cutting the log straight through it’s diameter, leaving the heart of the log creating less product waste. The unique blend of character and grain lends itself to the way lumber was cut centuries ago.
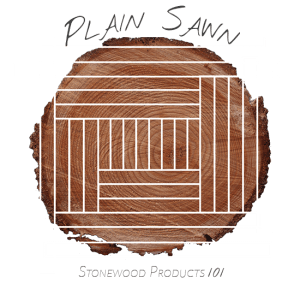
Plain Sawn (aka Flat Sawn) Plain sawn (aka flat sawn) is the most common lumber available. This is the most inexpensive way to manufacture logs into lumber. The annual rings are generally 30 degrees or less to the face of the board. The resulting wood displays a cathedral pattern on the face of the board.

Quarter Sawn QuarterSawn lumber is defined as wood where the annual growth rings intersect the face of the board at 60 to 90 degree angles. Each log is cut into quarters, then boards are cut from the circumference to the center.
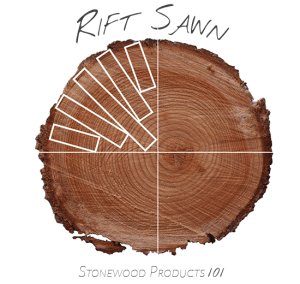
Rift Sawn: Lumber sawn so that the annual rings are typically between 30-60 degrees, with 45 degrees being ideal. Manufactured by milling perpendicular to the log’s growth rings produces a pattern with a linear grain and no flecking.
